AWS Beanstalk: 7 Powerful Reasons to Use This Ultimate Tool
If you’re diving into cloud computing, AWS Beanstalk is your secret weapon. It simplifies deployment, scales automatically, and lets developers focus on code—not infrastructure. Welcome to effortless cloud management.
What Is AWS Beanstalk and Why It Matters

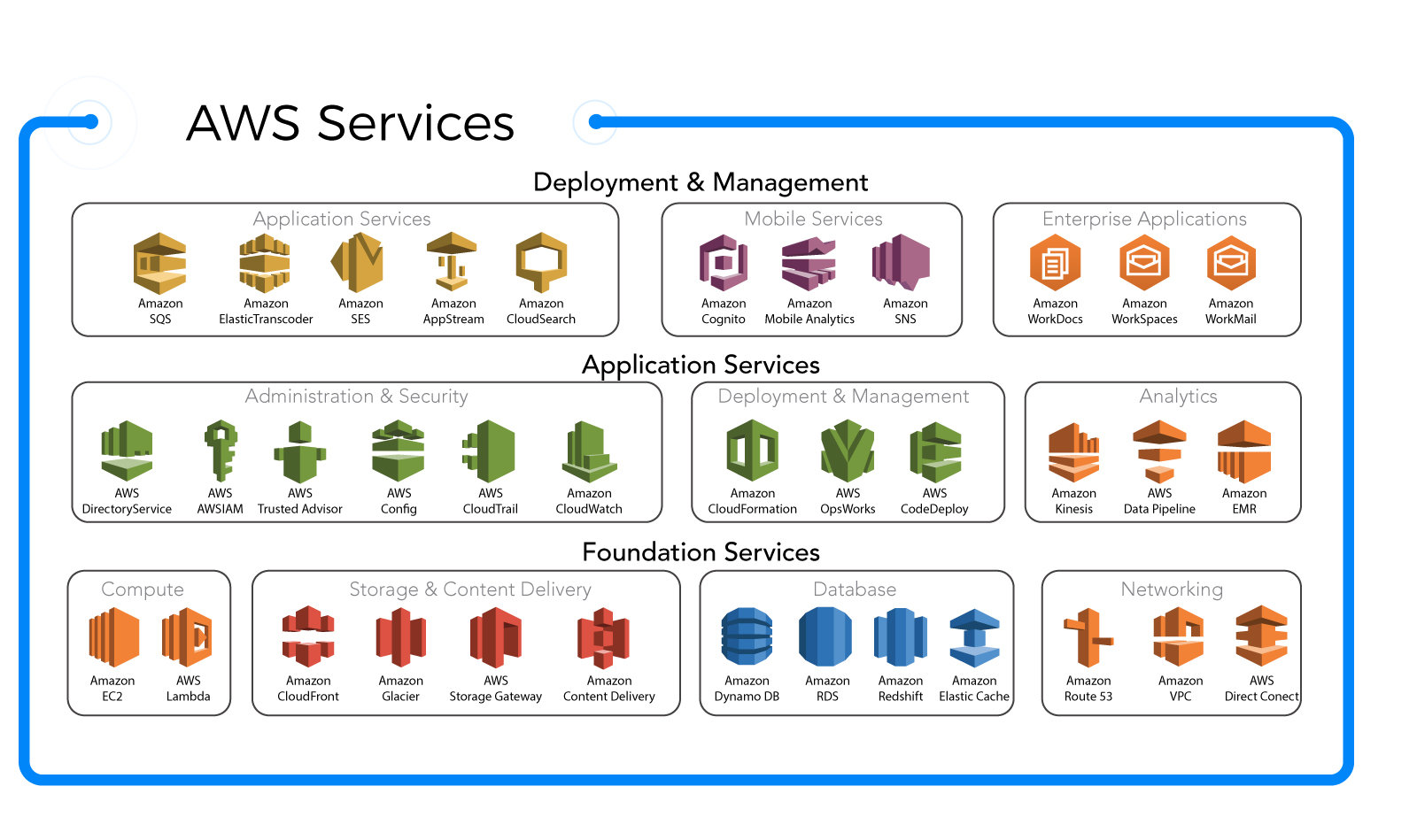
AWS Elastic Beanstalk, commonly referred to as AWS Beanstalk, is a Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS) offering from Amazon Web Services (AWS) that simplifies the deployment and management of applications in the cloud. It allows developers to upload their code, and AWS automatically handles the deployment, from capacity provisioning, load balancing, and auto-scaling to application health monitoring.
Core Definition and Purpose
AWS Beanstalk is not a server or a runtime environment itself, but rather a management layer that sits on top of AWS infrastructure services like EC2, S3, RDS, and ELB. Its primary purpose is to abstract the complexity of infrastructure management so developers can deploy applications quickly without needing deep DevOps expertise.
- Supports multiple languages: Java, .NET, PHP, Node.js, Python, Ruby, Go, and Docker.
- Automatically deploys applications using best practices for availability and scalability.
- Integrates seamlessly with other AWS services for databases, caching, and monitoring.
According to AWS’s official documentation, Elastic Beanstalk is designed to “make it easier for developers to quickly deploy and manage applications in the AWS Cloud.”
How AWS Beanstalk Differs from EC2 and Other AWS Services
While Amazon EC2 gives you full control over virtual servers, AWS Beanstalk takes a higher-level approach. With EC2, you manage the OS, security patches, scaling policies, and deployment scripts. With Beanstalk, you simply upload your code, and it handles the rest—while still allowing you to dive into the underlying resources when needed.
“Elastic Beanstalk enables you to focus on your application code rather than spending time on infrastructure management.” — AWS Official Site
Compared to services like AWS Lambda (serverless) or ECS (container orchestration), Beanstalk strikes a balance between control and convenience. It’s ideal for developers who want automation but aren’t ready to fully embrace serverless or Kubernetes.
Key Features That Make AWS Beanstalk a Game-Changer
AWS Beanstalk isn’t just about simplicity—it’s packed with powerful features that make it a top choice for startups and enterprises alike. From auto-scaling to environment management, it delivers enterprise-grade capabilities with minimal effort.
Automatic Scaling and Load Balancing
One of the standout features of AWS Beanstalk is its ability to automatically scale your application based on traffic. You can define scaling policies based on CPU usage, network traffic, or custom CloudWatch metrics.
- Supports both horizontal scaling (adding more instances) and vertical scaling (increasing instance size).
- Integrates with Elastic Load Balancing (ELB) to distribute traffic evenly across instances.
- Can scale from a single instance to hundreds, depending on demand.
This means your application can handle sudden traffic spikes—like during a product launch or viral marketing campaign—without manual intervention.
Environment Management and Configuration
AWS Beanstalk allows you to create multiple environments for the same application—such as development, staging, and production. Each environment can have different configurations, instance types, and scaling rules.
- Environments are isolated, reducing the risk of configuration drift.
- You can swap URLs between environments for zero-downtime deployments.
- Configuration templates let you save and reuse settings across projects.
This makes it easy to follow CI/CD best practices and maintain a clean deployment pipeline.
How AWS Beanstalk Works Under the Hood
Understanding the internal architecture of AWS Beanstalk helps you appreciate how it simplifies complex operations. Behind the scenes, it orchestrates a suite of AWS services to deliver a seamless experience.
The Role of EC2, S3, and CloudWatch
When you deploy an application to AWS Beanstalk, your code is stored in Amazon S3. Beanstalk then provisions EC2 instances based on your environment configuration. These instances pull the code from S3 and run your application.
- S3 acts as a secure, durable storage for your application versions.
- EC2 instances run your app and can be managed via Auto Scaling Groups.
- CloudWatch monitors application health, logs, and performance metrics.
If an instance fails, CloudWatch triggers a replacement via Auto Scaling, ensuring high availability.
Deployment Lifecycle Explained
The deployment process in AWS Beanstalk follows a clear lifecycle:
- You upload your application (ZIP file, WAR, or Docker image).
- Beanstalk stores it in S3 and creates a new application version.
- It deploys the version to your environment, launching or updating EC2 instances.
- Health checks are performed; if successful, traffic is routed to the new instances.
- Old instances are terminated (depending on deployment policy).
You can choose between several deployment strategies: All at Once, Rolling, Rolling with Additional Batch, or Immutable. Each offers a trade-off between speed and risk.
“With immutable deployments, AWS Beanstalk creates a completely new set of instances, ensuring no configuration drift and faster rollback if needed.” — AWS DevOps Best Practices
Supported Platforms and Languages in AWS Beanstalk
AWS Beanstalk supports a wide range of programming languages and platforms, making it versatile for different development teams and use cases.
Programming Languages and Runtimes
Beanstalk natively supports:
- Java (Tomcat or Java SE)
- .NET on Windows Server
- PHP (Apache)
- Node.js
- Python (WSGI)
- Ruby (Rack)
- Go
- Docker (single container or multi-container with ECS)
This flexibility means you don’t have to rewrite your application to use Beanstalk. Whether you’re running a legacy .NET app or a modern Node.js microservice, Beanstalk can handle it.
Custom Platforms and Docker Support
For teams using less common runtimes or needing full control, AWS Beanstalk supports custom platforms via Packer. You can define your own Amazon Machine Image (AMI) with specific software and configurations.
Additionally, Docker support allows you to deploy containerized applications. You can use a single Docker container or a multi-container environment orchestrated by Amazon ECS within Beanstalk.
This bridges the gap between traditional PaaS and container-based deployment, offering the best of both worlds.
Benefits of Using AWS Beanstalk for Your Applications
Choosing AWS Beanstalk comes with a host of advantages that can accelerate development, reduce costs, and improve reliability.
Developer Productivity and Faster Time-to-Market
By removing the need to manage infrastructure, Beanstalk allows developers to focus on writing code. This significantly reduces the time required to deploy new features or fix bugs.
- No need to write CloudFormation templates or Terraform scripts for basic setups.
- Integrated CI/CD pipelines can be set up with minimal configuration.
- Teams can deploy multiple times per day with confidence.
According to a case study by AWS, companies using Beanstalk report up to 50% faster deployment cycles.
Cost Efficiency and Resource Optimization
While AWS Beanstalk itself is free, you pay only for the underlying AWS resources (EC2, S3, RDS, etc.). This pay-as-you-go model ensures you’re not overpaying for idle capacity.
- Auto-scaling ensures you only run the number of instances needed.
- You can use Spot Instances or Reserved Instances to further reduce costs.
- Beanstalk’s monitoring helps identify underutilized resources.
For startups and small teams, this cost predictability is a major advantage over over-provisioning servers.
Common Use Cases and Real-World Applications of AWS Beanstalk
AWS Beanstalk is not just for simple web apps—it powers complex, high-traffic systems across industries.
Web Applications and APIs
One of the most common uses of AWS Beanstalk is hosting web applications and RESTful APIs. Whether it’s a company website, an e-commerce platform, or a backend API for a mobile app, Beanstalk provides a reliable, scalable foundation.
- Handles traffic spikes during sales or promotions.
- Supports HTTPS with integrated SSL/TLS certificates.
- Can be paired with RDS for database backend and ElastiCache for session storage.
For example, a fintech startup might use Beanstalk to deploy its customer-facing web portal while connecting to a secure RDS database for transaction processing.
Microservices and DevOps Pipelines
While Kubernetes is often associated with microservices, Beanstalk can also play a role—especially in early-stage or mid-sized microservices architectures.
- Each microservice can run in its own Beanstalk environment.
- Environments can be versioned and deployed independently.
- Integrates with AWS CodePipeline and CodeBuild for automated testing and deployment.
This allows teams to adopt DevOps practices without the complexity of managing Kubernetes clusters.
Challenges and Limitations of AWS Beanstalk
Despite its many benefits, AWS Beanstalk isn’t a one-size-fits-all solution. It has some limitations that teams should be aware of before adoption.
Less Control Compared to EC2 or ECS
Because Beanstalk abstracts infrastructure, you have less direct control over the underlying systems. While you can SSH into instances and modify configurations, some advanced networking or security settings may require workarounds.
- Custom kernel modules or low-level OS tweaks are difficult.
- Networking configurations are limited compared to VPC-native services.
- Debugging can be harder due to abstraction layers.
Teams with strict compliance or performance requirements may find Beanstalk too restrictive.
Deprecation of Some Platforms and Vendor Lock-In
AWS has deprecated certain platforms over time (e.g., older PHP versions), which can force migration efforts. Additionally, heavy reliance on Beanstalk-specific configurations (like .ebextensions) can lead to vendor lock-in.
“While Beanstalk speeds up deployment, it can make migration to other clouds more challenging.” — Cloud Architecture Best Practices
To mitigate this, it’s recommended to keep infrastructure-as-code portable and avoid hardcoding AWS-specific logic in your application.
Best Practices for Maximizing AWS Beanstalk Performance
To get the most out of AWS Beanstalk, follow these proven best practices that enhance performance, security, and maintainability.
Use Configuration Files (.ebextensions)
The .ebextensions directory allows you to customize your environment with configuration files written in YAML or JSON. You can use them to:
- Install additional software (e.g., ImageMagick, FFmpeg).
- Set environment variables securely.
- Configure nginx or Apache settings.
- Run scripts during deployment.
Example: .ebextensions/01-install-packages.config can install system packages automatically during deployment.
Enable Enhanced Health Reporting and Monitoring
AWS Beanstalk offers basic and enhanced health reporting. Enhanced health provides detailed insights into request rates, latency, and instance health.
- Integrate with CloudWatch Alarms for proactive notifications.
- Use AWS X-Ray for distributed tracing in microservices.
- Enable log streaming to CloudWatch Logs for real-time debugging.
These tools help you detect and resolve issues before users are affected.
How to Get Started with AWS Beanstalk: A Step-by-Step Guide
Ready to deploy your first application? Here’s a quick walkthrough to get you started.
Creating Your First Application
1. Log in to the AWS Management Console.
2. Navigate to the Elastic Beanstalk service.
3. Click “Create Application.”
4. Enter a name and description.
5. Choose a platform (e.g., Python 3.9).
6. Upload your code (ZIP file or connect to a code repository).
7. Click “Create.”
AWS will provision the environment and deploy your app. In a few minutes, you’ll have a live URL.
Deploying and Managing Environments
Once your app is live, you can:
- Add a custom domain with Route 53 and ACM for SSL.
- Scale manually or set auto-scaling rules.
- Update the application by uploading a new version.
- Roll back to a previous version if needed.
You can also use the AWS CLI or SDKs to automate deployments, making it ideal for integration into CI/CD pipelines.
What is AWS Beanstalk used for?
AWS Beanstalk is used to deploy and manage web applications and services in the AWS Cloud without worrying about infrastructure. Developers upload their code, and Beanstalk handles provisioning, scaling, load balancing, and monitoring automatically.
Is AWS Beanstalk free to use?
AWS Beanstalk itself is free. You only pay for the underlying AWS resources your application consumes, such as EC2 instances, S3 storage, RDS databases, and data transfer.
How does AWS Beanstalk compare to AWS Lambda?
Beanstalk is ideal for traditional web apps that run continuously, while Lambda is for event-driven, short-lived functions. Beanstalk offers more control and persistent environments, whereas Lambda is serverless and scales to zero.
Can I use Docker with AWS Beanstalk?
Yes, AWS Beanstalk supports both single-container and multi-container Docker environments. Multi-container setups use Amazon ECS in the background for orchestration.
What happens when an instance fails in AWS Beanstalk?
If an EC2 instance fails, AWS Beanstalk detects it through health checks and automatically replaces it using Auto Scaling. This ensures high availability and minimal downtime.
In conclusion, AWS Beanstalk is a powerful, developer-friendly service that bridges the gap between infrastructure and application code. It automates deployment, scales effortlessly, and integrates deeply with the AWS ecosystem. While it may not suit every use case—especially those requiring fine-grained control—it remains an excellent choice for teams looking to ship code faster and operate reliably in the cloud. Whether you’re launching a startup or managing enterprise applications, AWS Beanstalk offers a compelling blend of simplicity and power.
Further Reading: