AWS Cloud: 7 Powerful Reasons to Dominate the Future
Welcome to the world of AWS Cloud, where innovation meets scalability. Whether you’re a startup or a global enterprise, understanding AWS Cloud is your first step toward digital transformation. Let’s dive into why it’s revolutionizing the tech landscape.
What Is AWS Cloud and Why It Matters

Amazon Web Services (AWS) Cloud is the world’s most comprehensive and widely adopted cloud platform. Launched in 2006, AWS offers over 200 fully featured services from data centers globally. These services span computing, storage, networking, databases, analytics, machine learning, security, and more. Businesses use AWS Cloud to reduce costs, increase agility, and scale applications seamlessly.
Origins and Evolution of AWS Cloud
AWS began as an internal solution to Amazon’s scalability challenges. As Amazon’s e-commerce platform grew, it needed a more flexible and resilient infrastructure. Instead of relying on traditional data centers, Amazon built a distributed, virtualized system. In 2006, it launched Amazon S3 (Simple Storage Service) and EC2 (Elastic Compute Cloud), marking the birth of the modern public cloud era.
- AWS started with just storage and compute services.
- By 2010, it expanded into databases, content delivery, and security.
- Today, AWS powers millions of applications worldwide, including Netflix, Airbnb, and NASA.
“AWS didn’t just enter the market — it created the market for cloud computing.” — Andy Jassy, CEO of Amazon
Core Components of AWS Cloud Architecture
The AWS Cloud is built on a global infrastructure of Regions, Availability Zones, and Edge Locations. This architecture ensures high availability, fault tolerance, and low latency.
- Regions: Geographical areas like US East (N. Virginia), EU (Frankfurt), or Asia Pacific (Tokyo).
- Availability Zones (AZs): Isolated data centers within a Region, connected via low-latency links.
- Edge Locations: Points of presence for caching content using Amazon CloudFront.
Each component plays a vital role in delivering reliable and performant cloud services. For example, deploying applications across multiple AZs ensures uptime even during hardware failures.
Top 7 Benefits of Using AWS Cloud
The dominance of AWS Cloud isn’t accidental. It stems from tangible benefits that directly impact business performance, innovation speed, and operational efficiency. Here are seven powerful reasons why organizations choose AWS.
1. Unmatched Scalability and Elasticity
One of the biggest advantages of AWS Cloud is its ability to scale on demand. Whether you need to handle a sudden traffic spike or expand globally, AWS allows you to provision resources in minutes.
- Auto Scaling adjusts compute capacity based on real-time demand.
- Amazon EC2 instances can be launched or terminated automatically.
- Services like AWS Lambda enable serverless computing, scaling to zero when idle.
This elasticity means you only pay for what you use, avoiding over-provisioning and wasted resources.
2. Cost Efficiency and Pay-as-You-Go Pricing
Traditional IT infrastructure requires large upfront investments in hardware and maintenance. AWS Cloud eliminates this with a pay-as-you-go model.
- No long-term contracts or upfront payments.
- Prices decrease as usage increases (volume discounts).
- Reserved Instances offer up to 75% savings for predictable workloads.
According to a 2023 AWS report, organizations save an average of 30–50% on IT costs after migrating to the cloud.
3. Global Reach and High Availability
AWS operates in 33 geographic Regions and 102 Availability Zones as of 2024, with plans to expand further. This global footprint enables businesses to deploy applications closer to their users, reducing latency and improving performance.
- Deploy workloads in multiple Regions for disaster recovery.
- Use Route 53 for global DNS routing and traffic management.
- Leverage AWS Global Accelerator to improve application availability and performance.
For multinational companies, this means faster load times and better user experiences across continents.
4. Security and Compliance Leadership
Security is a top priority for AWS. The platform is designed with multiple layers of protection, including encryption, identity management, threat detection, and compliance certifications.
- AWS complies with over 140 security standards and certifications (e.g., ISO 27001, HIPAA, GDPR).
- Shared Responsibility Model clarifies security roles: AWS secures the infrastructure; customers secure their data and applications.
- Tools like AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM), AWS Shield (DDoS protection), and AWS WAF (Web Application Firewall) enhance security posture.
As stated on the official AWS Security page, “Security is job zero” — meaning it’s the highest priority across all services.
5. Innovation at Speed with Advanced Services
AWS continuously introduces new services and features, enabling rapid innovation. From artificial intelligence to quantum computing, AWS provides tools that were once accessible only to tech giants.
- Amazon SageMaker simplifies machine learning model development.
- Amazon Rekognition offers image and video analysis.
- Amazon Quantum Ledger Database (QLDB) supports immutable transaction logs.
With over 2,000 new features launched annually, AWS empowers developers to build cutting-edge solutions faster.
6. Robust Ecosystem and Partner Network
AWS has built one of the largest ecosystems in the tech industry. This includes technology partners, consulting firms, training providers, and marketplaces.
- AWS Marketplace offers thousands of pre-configured software solutions.
- APN (AWS Partner Network) includes over 120,000 partners worldwide.
- Training and certification programs help professionals gain in-demand cloud skills.
This ecosystem reduces time-to-market and lowers implementation risks for enterprises.
7. Sustainability and Environmental Responsibility
AWS is committed to sustainability. It aims to power its operations with 100% renewable energy by 2025 and achieve net-zero carbon emissions by 2040.
- AWS has launched wind and solar farms across the globe.
- Data centers are designed for energy efficiency, using advanced cooling and power management.
- Customers benefit from AWS’s scale — cloud computing is up to 80% more energy-efficient than on-premises data centers.
Learn more about AWS’s sustainability goals at sustainability.aboutamazon.com.
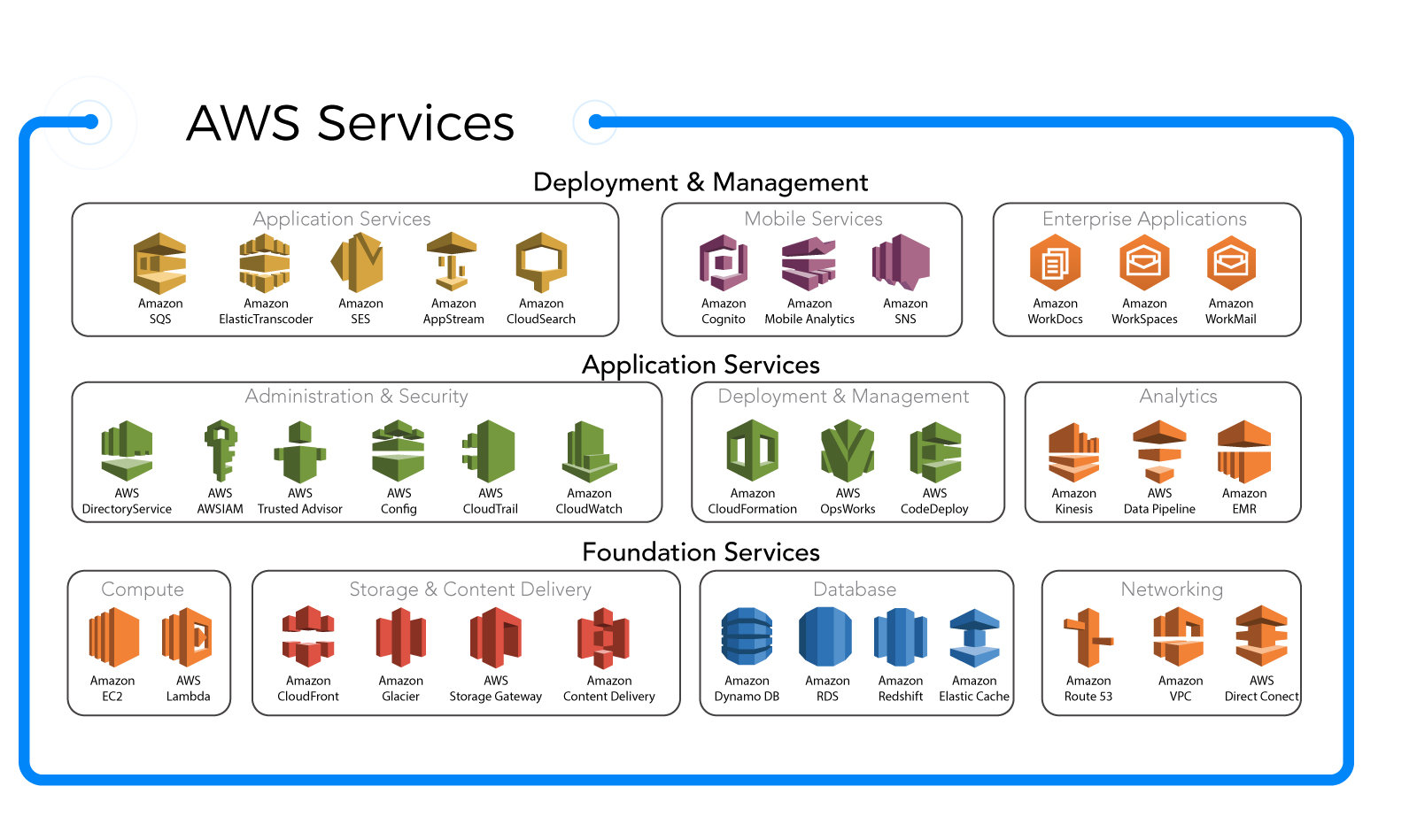
AWS Cloud Services: A Deep Dive into Key Offerings
AWS Cloud offers a vast array of services. Understanding the core categories helps organizations choose the right tools for their needs. Let’s explore the most essential services.
Compute Services: Powering Your Applications
Compute services provide the processing power needed to run applications. AWS offers flexible options depending on workload requirements.
- Amazon EC2: Virtual servers in the cloud with customizable CPU, memory, storage, and networking.
- AWS Lambda: Run code without provisioning servers — ideal for event-driven tasks.
- Amazon ECS & EKS: Container management using Docker and Kubernetes.
These services support everything from simple websites to complex microservices architectures.
Storage Solutions: Secure and Scalable Data Management
Data is the lifeblood of modern businesses. AWS provides durable, secure, and scalable storage options.
- Amazon S3: Object storage for backups, media files, and big data analytics. Offers 99.999999999% durability.
- Amazon EBS: Block storage for EC2 instances, ideal for databases.
- Amazon Glacier: Low-cost archival storage for long-term retention.
With features like versioning, lifecycle policies, and cross-region replication, S3 is a cornerstone of AWS Cloud.
Networking and Content Delivery
Efficient networking ensures fast, secure, and reliable communication between services and users.
- Amazon VPC: Create isolated virtual networks in the cloud.
- AWS Direct Connect: Establish private connections between on-premises and AWS.
- Amazon CloudFront: CDN that delivers content with low latency using edge locations.
These services are critical for hybrid cloud setups and global application delivery.
How AWS Cloud Compares to Competitors
While AWS Cloud leads the market, it faces strong competition from Microsoft Azure and Google Cloud Platform (GCP). Understanding the differences helps organizations make informed decisions.
Market Share and Industry Leadership
According to Synergy Research Group (2024), AWS holds a 32% share of the global cloud infrastructure market — significantly ahead of Azure (23%) and GCP (11%).
- AWS has been the market leader since cloud computing began.
- Its first-mover advantage allowed it to build deep expertise and a broad service portfolio.
- Many startups and enterprises standardize on AWS due to its maturity and reliability.
Despite growing competition, AWS Cloud remains the benchmark for innovation and scale.
Service Breadth vs. Integration Strength
AWS excels in service breadth, offering more tools and features than any competitor. Azure, however, shines in integration with Microsoft products like Office 365 and Active Directory.
- AWS is ideal for organizations seeking flexibility and best-of-breed solutions.
- Azure is preferred by enterprises already invested in Microsoft ecosystems.
- GCP leads in data analytics and machine learning, especially for AI-native applications.
The choice often depends on existing IT investments and strategic goals.
Pricing Models and Cost Management Tools
All three providers use pay-as-you-go pricing, but cost structures vary. AWS offers granular control over spending with tools like AWS Cost Explorer and Budgets.
- AWS provides detailed billing reports and cost allocation tags.
- Azure has hybrid benefits for customers using Windows Server and SQL Server.
- GCP offers sustained use discounts and custom machine types.
While AWS may appear more complex, its transparency and optimization tools help businesses manage costs effectively.
Real-World Use Cases of AWS Cloud
Theoretical benefits are compelling, but real-world applications prove AWS Cloud’s value. Let’s examine how different industries leverage AWS.
Startups and SaaS Companies
Startups use AWS Cloud to launch quickly and scale affordably. With no upfront infrastructure costs, they can focus on product development.
- Slack migrated to AWS to handle rapid user growth.
- Canva uses AWS to deliver real-time design collaboration to millions.
- Many SaaS platforms use AWS Lambda and API Gateway for serverless backends.
The agility of AWS Cloud allows startups to iterate fast and respond to market changes.
Enterprise IT and Digital Transformation
Large enterprises use AWS Cloud to modernize legacy systems, improve resilience, and enable remote work.
- GE Aviation moved mission-critical systems to AWS for better data analytics.
- Unilever uses AWS to power its global supply chain and AI-driven marketing.
- Siemens leverages AWS IoT services for industrial automation.
Through cloud migration, enterprises reduce downtime, enhance security, and accelerate innovation.
Media and Entertainment
The media industry relies on AWS Cloud for content creation, distribution, and streaming.
- Netflix runs entirely on AWS, serving over 200 million subscribers.
- Disney+ uses AWS for video encoding, storage, and global delivery.
- BBC uses AWS for live event broadcasting and archive digitization.
Services like Amazon Elemental MediaLive and MediaConvert enable broadcast-quality streaming at scale.
Getting Started with AWS Cloud: A Step-by-Step Guide
Beginning your AWS Cloud journey doesn’t have to be overwhelming. Follow these steps to get started confidently.
1. Create an AWS Account
Visit aws.amazon.com and sign up for a free account. You’ll need a credit card, but many services are free for 12 months under the AWS Free Tier.
- Choose the “Basic” plan to start.
- Verify your email and phone number.
- Set up multi-factor authentication (MFA) for security.
2. Explore the AWS Management Console
The AWS Management Console is your central hub for managing services. It features a user-friendly dashboard with access to all AWS resources.
- Use the search bar to find services quickly.
- Navigate using the Services menu (e.g., EC2, S3, IAM).
- Switch between Regions using the dropdown in the top-right corner.
3. Launch Your First EC2 Instance
Amazon EC2 is a great starting point. Here’s how to launch a virtual server:
- Go to EC2 Dashboard > Instances > Launch Instance.
- Choose an Amazon Machine Image (AMI), like Amazon Linux 2023.
- Select an instance type (e.g., t3.micro — free tier eligible).
- Configure security groups to allow SSH or HTTP access.
- Review and launch, then download your key pair (.pem file).
Once running, you can connect via SSH and begin installing applications.
4. Learn AWS with Free Training
AWS provides extensive learning resources:
- AWS Training and Certification offers free digital courses.
- AWS Skill Builder has over 500 learning paths.
- Hands-on labs and sandbox environments help practice without risk.
Start with the “AWS Cloud Practitioner Essentials” course to build foundational knowledge.
Common Challenges and How to Overcome Them
While AWS Cloud offers immense benefits, users may face challenges. Awareness and preparation can mitigate these issues.
Complexity and Learning Curve
With over 200 services, AWS can feel overwhelming. New users often struggle with navigation and service selection.
- Solution: Start with core services (EC2, S3, IAM) and expand gradually.
- Use AWS Well-Architected Framework to design reliable systems.
- Leverage AWS documentation and community forums.
Cost Management and Unexpected Bills
Without proper monitoring, cloud costs can spiral. Some users report surprise bills due to misconfigured resources.
- Solution: Enable AWS Budgets and Cost Explorer.
- Use tagging to track spending by department or project.
- Shut down unused resources (e.g., idle EC2 instances).
Regular audits and alerts help maintain financial control.
Security Misconfigurations
Human error is a leading cause of cloud breaches. Misconfigured S3 buckets or overly permissive IAM roles can expose data.
- Solution: Implement least-privilege access with IAM policies.
- Use AWS Config to monitor compliance.
- Enable AWS GuardDuty for threat detection.
Security should be proactive, not reactive.
The Future of AWS Cloud: Trends and Predictions
AWS Cloud continues to evolve. Emerging trends will shape how businesses use the cloud in the coming years.
Rise of Serverless and Event-Driven Architectures
Serverless computing with AWS Lambda is gaining traction. It allows developers to focus on code, not infrastructure.
- Event-driven models improve efficiency and reduce costs.
- Integration with services like S3, DynamoDB, and API Gateway simplifies development.
- Expect more managed services to adopt serverless backends.
AI and Machine Learning Democratization
AWS is making AI accessible to non-experts. Services like Amazon SageMaker and Bedrock lower the barrier to entry.
- Pre-trained models for vision, language, and forecasting.
- Generative AI tools for creating content, code, and customer experiences.
- Customizable foundation models for enterprise use cases.
AI will become a standard feature in applications built on AWS Cloud.
Edge Computing and IoT Expansion
As devices generate more data, processing at the edge becomes critical. AWS offers services like AWS Greengrass and Wavelength.
- Greengrass extends AWS to on-premises devices.
- Wavelength integrates with 5G networks for ultra-low latency.
- IoT Core manages billions of connected devices securely.
The convergence of cloud, edge, and 5G will unlock new possibilities in manufacturing, healthcare, and smart cities.
What is AWS Cloud?
AWS Cloud is Amazon’s cloud computing platform, offering over 200 services including computing, storage, databases, and machine learning. It enables businesses to innovate faster, scale efficiently, and reduce IT costs.
How much does AWS Cloud cost?
AWS uses a pay-as-you-go model with no upfront fees. Many services are free for 12 months under the AWS Free Tier. Actual costs depend on usage, but tools like AWS Pricing Calculator help estimate expenses.
Is AWS Cloud secure?
Yes, AWS Cloud is highly secure. It complies with global standards like ISO 27001, HIPAA, and GDPR. AWS follows a Shared Responsibility Model, where AWS secures the infrastructure and customers secure their data and applications.
Can I migrate my existing applications to AWS Cloud?
Absolutely. AWS provides migration tools like AWS Server Migration Service (SMS) and Database Migration Service (DMS). Many organizations successfully migrate on-premises systems to AWS with minimal downtime.
What certifications should I get for AWS Cloud?
Popular AWS certifications include AWS Certified Cloud Practitioner (entry-level), AWS Solutions Architect – Associate, and AWS Developer – Associate. These validate your skills and boost career prospects.
The AWS Cloud is more than just a technology platform — it’s a catalyst for innovation, efficiency, and growth. From startups to Fortune 500 companies, organizations worldwide rely on AWS to stay competitive. With its unmatched scalability, robust security, global reach, and continuous innovation, AWS Cloud remains the leader in the cloud computing era. Whether you’re just starting or scaling globally, embracing AWS Cloud is a strategic move toward a more agile and future-ready business.
Further Reading: