AWS Glue: 7 Powerful Features You Must Know in 2024
Ever felt overwhelmed by messy data scattered across systems? AWS Glue is your ultimate solution—a fully managed ETL service that simplifies data integration. Let’s dive into how it transforms raw data into gold.
What Is AWS Glue and Why It Matters

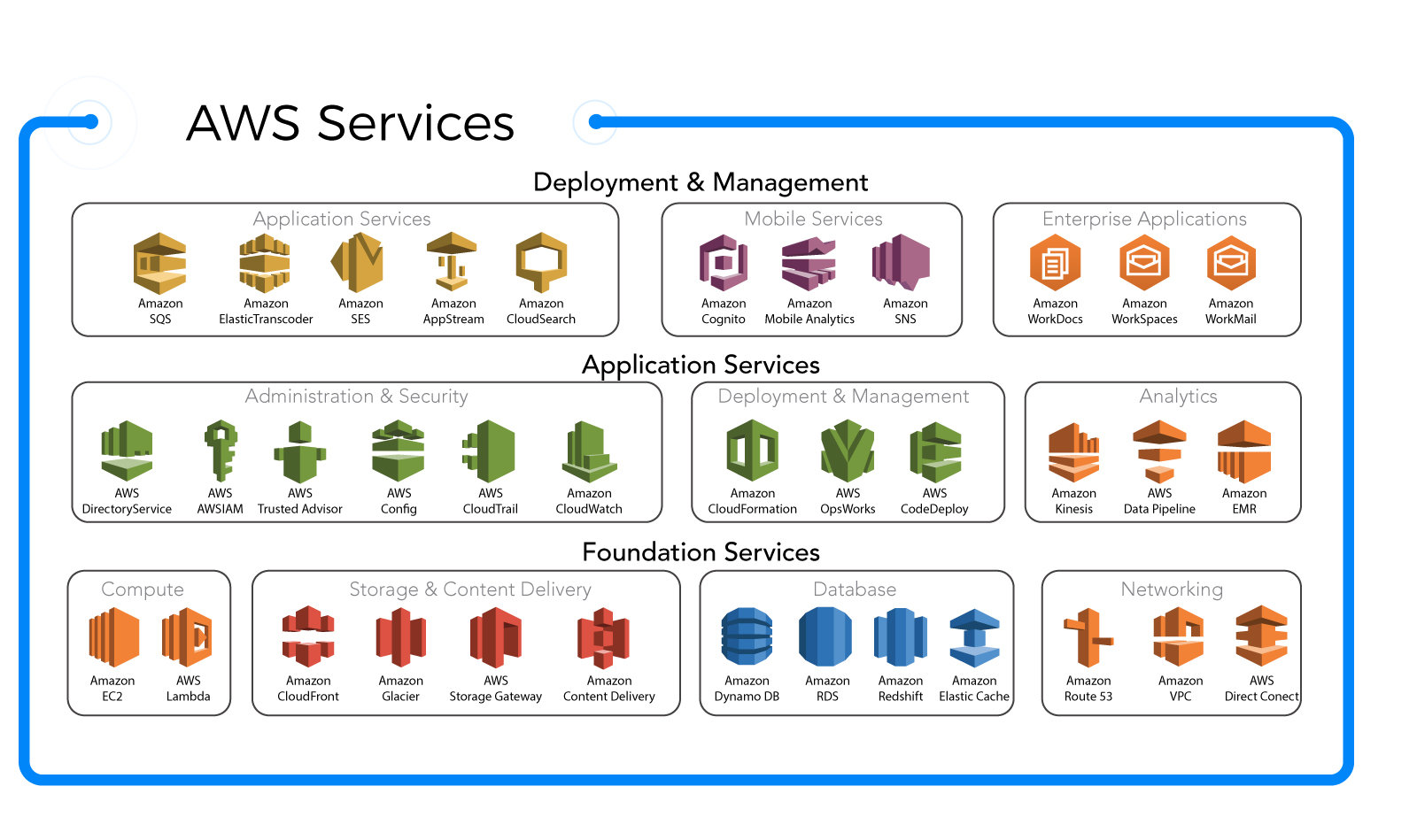
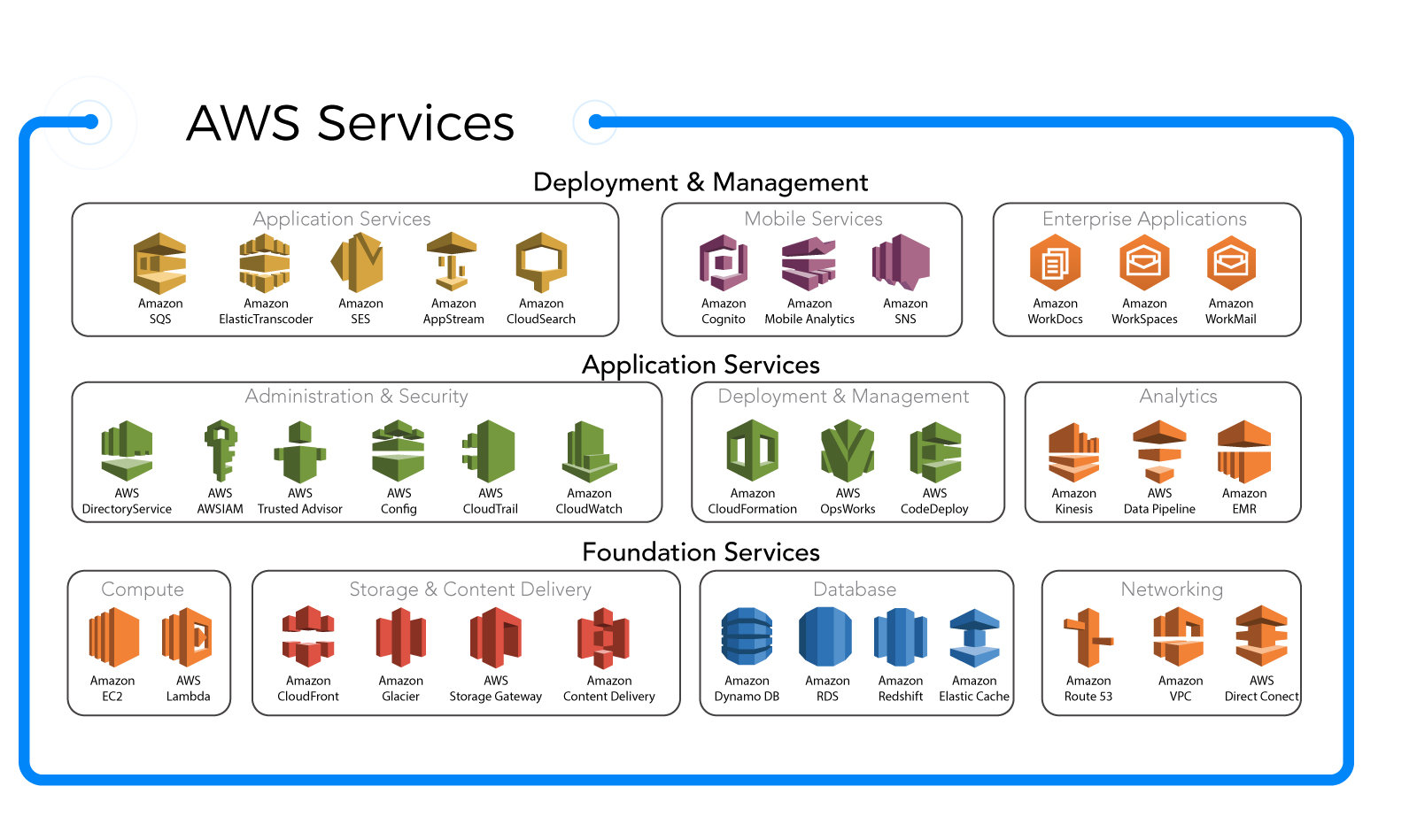
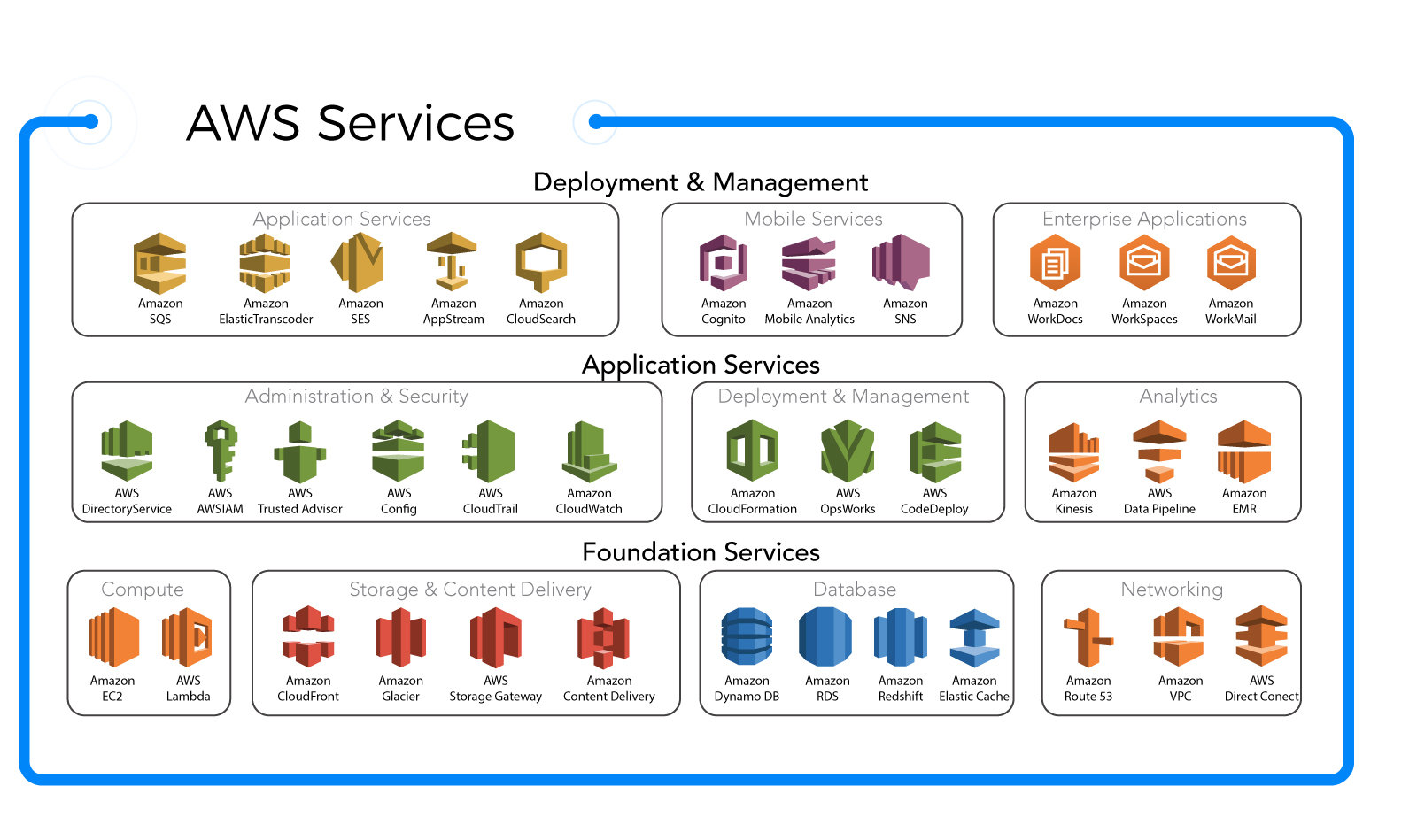
AWS Glue is a serverless data integration service from Amazon Web Services (AWS) that makes it easy to discover, prepare, and combine data for analytics, machine learning, and application development. It automates the time-consuming tasks of data integration, allowing developers and data engineers to focus on insights rather than infrastructure.
Core Definition and Purpose
AWS Glue is designed to handle Extract, Transform, and Load (ETL) operations at scale. It automatically generates code in Python or Scala to move and transform data, reducing manual coding effort. By using a central metadata repository called the Data Catalog, AWS Glue enables seamless data discovery and governance.
- Automates ETL workflows for structured and semi-structured data
- Integrates with various AWS and third-party data sources
- Supports both batch and streaming data processing
“AWS Glue removes the heavy lifting from data preparation, making it accessible even to teams without deep programming expertise.” — AWS Official Documentation
Evolution of AWS Glue
Launched in 2017, AWS Glue was introduced to address the growing complexity of data pipelines in the cloud. Over the years, it has evolved with features like Glue Studio, Glue DataBrew, and Glue Elastic Views, enhancing usability and performance.
- 2017: Initial release with ETL automation and Data Catalog
- 2020: Introduction of AWS Glue Studio for visual workflow design
- 2021: Launch of Glue DataBrew for visual data preparation
- 2022: Glue Elastic Views for materialized views across sources
These updates reflect AWS’s commitment to simplifying data integration for enterprises of all sizes. You can learn more about its evolution on the official AWS Glue page.
Key Components of AWS Glue
To fully leverage AWS Glue, it’s essential to understand its core components. Each plays a critical role in building scalable and efficient data pipelines.
Data Catalog and Crawlers
The AWS Glue Data Catalog acts as a persistent metadata store, similar to Apache Hive’s metastore. It stores table definitions, schema information, and partition details. Crawlers automatically scan data sources—like Amazon S3, RDS, or Redshift—and populate the catalog with metadata.
- Crawlers detect schema changes and update the catalog automatically
- Supports custom classifiers for non-standard data formats
- Enables schema versioning and governance
For example, a crawler can scan a folder in S3 containing JSON logs and create a table with fields like timestamp, user_id, and event_type. This eliminates the need for manual schema definition.
ETL Jobs and Script Generation
AWS Glue ETL jobs are the workhorses that transform and load data. When you create a job, Glue automatically generates Python PySpark or Scala Spark code based on your source and target data. You can customize this code or write your own.
- Jobs run on fully managed Apache Spark environments
- Supports incremental data processing using job bookmarks
- Allows integration with external libraries via custom scripts
These jobs can be triggered on a schedule, via events, or through APIs, making them highly flexible for different use cases.
Triggers and Workflows
Triggers control when ETL jobs run. They can be scheduled (cron-based), event-driven (e.g., S3 upload), or conditional (e.g., after another job completes). Workflows allow you to orchestrate multiple jobs, crawlers, and triggers into a single, visual pipeline.
- Workflows provide dependency management and error handling
- Support parallel and sequential execution paths
- Enable monitoring and debugging of end-to-end pipelines
This orchestration capability is crucial for complex data pipelines involving multiple stages of transformation and validation.
How AWS Glue Works: Step-by-Step Process
Understanding the workflow of AWS Glue helps in designing efficient data integration solutions. The process typically follows a sequence: crawl, catalog, transform, and load.
Step 1: Setting Up Data Sources
The first step is connecting AWS Glue to your data sources. Supported sources include Amazon S3, Amazon RDS, Amazon DynamoDB, JDBC-compatible databases, and more. You define connections with network and authentication details.
- Use VPC endpoints for secure access to private databases
- Configure IAM roles for least-privilege access
- Test connections before running crawlers
For instance, to connect to an RDS instance, you need the JDBC URL, username, password, and a security group that allows Glue access.
Step 2: Running Crawlers to Populate the Data Catalog
Once connections are set, crawlers scan the data sources. They infer schema, detect data types, and classify files (e.g., JSON, CSV, Parquet). The metadata is then stored in the Data Catalog as tables.
- Crawlers can run on-demand or on a schedule
- Support for custom regex-based classifiers
- Automatic detection of partitioned data (e.g., S3 paths like year=2023/month=01)
This step is crucial for enabling query engines like Amazon Athena or Amazon Redshift Spectrum to query the data without manual schema creation.
Step 3: Creating and Running ETL Jobs
With metadata in place, you can create ETL jobs. AWS Glue Studio provides a drag-and-drop interface to define transformations like filtering, joining, aggregating, or enriching data. Glue then generates the underlying Spark code.
- Use built-in transforms like
ApplyMapping,DropNullFields, orJoin - Add custom Python or Scala code for complex logic
- Preview data during development using Glue Studio’s data preview feature
Jobs can be tested in development endpoints before deployment to production, ensuring reliability.
Advanced Features of AWS Glue
Beyond basic ETL, AWS Glue offers advanced capabilities that enhance performance, scalability, and ease of use.
AWS Glue Studio: Visual ETL Development
Glue Studio simplifies ETL development with a visual interface. You can create jobs by dragging and dropping data sources, transformations, and sinks. It supports both batch and streaming jobs (using Apache Spark Structured Streaming).
- Real-time data preview during job design
- Integrated script editor with syntax highlighting
- Support for job templates and reusable components
This is especially helpful for teams transitioning from traditional ETL tools to cloud-native solutions.
AWS Glue DataBrew: No-Code Data Preparation
Glue DataBrew allows users to clean and normalize data visually, without writing code. It provides over 250 built-in transformations for handling missing values, standardizing formats, and detecting anomalies.
- Interactive data profiling with histograms and statistics
- One-click suggestions for common cleaning tasks
- Integration with Glue ETL jobs for end-to-end pipelines
DataBrew is ideal for data analysts and business users who need to prepare data before analysis.
AWS Glue Elastic Views: Combine Data Across Sources
Glue Elastic Views lets you create materialized views that combine data from multiple sources (e.g., DynamoDB and S3) into a single, queryable dataset. It uses SQL to define the view and automatically handles data replication and updates.
- Eliminates the need for complex ETL jobs for simple joins
- Supports near-real-time data synchronization
- Reduces latency for analytics queries
This feature is powerful for building unified customer views or operational dashboards.
Use Cases and Real-World Applications of AWS Glue
AWS Glue is used across industries for various data integration challenges. Here are some common scenarios where it shines.
Data Lake Construction on Amazon S3
Organizations use AWS Glue to build and manage data lakes. Crawlers catalog data from various sources, ETL jobs transform it into optimized formats (like Parquet or ORC), and the Data Catalog enables discovery and querying.
- Convert raw CSV files into columnar formats for faster queries
- Enforce data quality rules during transformation
- Apply partitioning and compression for cost efficiency
For example, a retail company might use Glue to ingest sales data from POS systems, transform it, and load it into S3 for analysis with Athena.
Migrating On-Premises Data to the Cloud
During cloud migration, AWS Glue helps move data from on-premises databases to AWS. It can connect via AWS Direct Connect or VPN and perform one-time or ongoing replication.
- Minimize downtime with incremental data sync
- Transform legacy schemas to modern data models
- Validate data consistency post-migration
A financial institution might use Glue to migrate customer records from an Oracle database to Amazon Redshift.
Streaming Data Integration with Kinesis and Kafka
With support for Apache Kafka and Amazon Kinesis, AWS Glue can process streaming data in near real time. This is useful for log analysis, IoT data, and real-time monitoring.
- Ingest data from MSK (Managed Streaming for Kafka)
- Apply transformations like filtering or aggregation
- Load results into data warehouses or analytics services
A media company might use Glue to process viewer engagement data from a mobile app in real time.
Performance Optimization and Best Practices
To get the most out of AWS Glue, it’s important to follow best practices for performance, cost, and reliability.
Optimizing Job Performance
Glue jobs run on Spark, so tuning Spark configurations can significantly improve performance. Key strategies include:
- Choosing the right worker type (G.1X vs G.2X) based on memory and CPU needs
- Using job bookmarks to process only new data
- Partitioning input data to enable parallel processing
Also, enabling continuous logging helps identify bottlenecks in job execution.
Cost Management Strategies
AWS Glue is billed per DPU (Data Processing Unit) hour. To control costs:
- Right-size DPUs based on job complexity
- Use Glue Development Endpoints only during active development
- Monitor job duration and optimize inefficient scripts
Setting up CloudWatch alarms for long-running jobs can prevent unexpected charges.
Data Security and Compliance
Security is critical when handling sensitive data. AWS Glue integrates with AWS IAM, KMS, and Lake Formation for comprehensive security.
- Encrypt data at rest using AWS KMS keys
- Use Lake Formation to define fine-grained access controls
- Enable audit logging with AWS CloudTrail
These measures help meet compliance requirements like GDPR, HIPAA, or SOC 2.
Integrations and Ecosystem Compatibility
AWS Glue doesn’t work in isolation—it’s part of a broader data ecosystem on AWS.
Integration with Amazon S3 and Athena
Amazon S3 is the most common data source and target for AWS Glue. Once data is cataloged, Amazon Athena can query it using standard SQL. This combination forms the backbone of many data lake architectures.
- Athena uses the Glue Data Catalog as its metadata store
- Glue jobs can optimize S3 data for Athena queries (e.g., partitioning, format conversion)
- Supports federated queries across multiple sources
Learn more about this integration in the Athena and Glue documentation.
Connection with Amazon Redshift and Snowflake
For data warehousing, AWS Glue can load transformed data into Amazon Redshift. It also supports external destinations like Snowflake via JDBC.
- Use Redshift as a target for analytics-ready datasets
- Leverage Glue’s built-in Redshift connectors for efficient loading
- Supports bulk inserts and upserts (via staging tables)
This enables hybrid cloud data architectures with seamless data flow.
Support for Open-Source and Third-Party Tools
AWS Glue supports integration with open-source frameworks and third-party tools:
- Run custom Python libraries in ETL jobs
- Use Apache Airflow (via MWAA) to orchestrate Glue jobs
- Connect to BI tools like Tableau or Power BI through Redshift or Athena
This flexibility ensures Glue fits into diverse technology stacks.
Common Challenges and How to Overcome Them
While AWS Glue is powerful, users may face certain challenges during implementation.
Handling Schema Evolution
Data schemas often change—new fields are added, types are modified. AWS Glue crawlers can detect these changes, but jobs may fail if not handled properly.
- Use schema versioning in the Data Catalog
- Implement error handling in ETL scripts (e.g., try-catch blocks)
- Leverage Glue’s schema registry for streaming data
Testing jobs with sample data that includes schema variations can prevent runtime failures.
Debugging and Monitoring Jobs
Debugging Glue jobs can be tricky due to the managed nature of the service. However, AWS provides tools to help.
- Use CloudWatch Logs to view job execution details
- Enable Glue job metrics for performance monitoring
- Use development endpoints for interactive debugging
Setting up alerts for job failures ensures quick response to issues.
Managing Dependencies and Workflows
Complex pipelines often involve multiple interdependent jobs. Without proper orchestration, this can lead to failures.
- Use Glue Workflows to define dependencies visually
- Implement retry logic for transient failures
- Document data lineage for audit and troubleshooting
Well-structured workflows improve maintainability and reduce operational overhead.
What is AWS Glue used for?
AWS Glue is used for automating data integration tasks like ETL (Extract, Transform, Load). It helps catalog data, clean and transform it, and load it into data lakes, warehouses, or analytics services. Common uses include building data lakes, migrating databases, and processing streaming data.
Is AWS Glue serverless?
Yes, AWS Glue is a fully serverless service. You don’t need to manage servers or clusters. AWS automatically provisions and scales the underlying Apache Spark environment based on job requirements.
How much does AWS Glue cost?
AWS Glue pricing is based on DPU (Data Processing Unit) hours for ETL jobs, crawler runtime, and Data Catalog usage. Development endpoints are billed hourly. There’s no upfront cost, and you pay only for what you use. Detailed pricing can be found on the AWS Glue pricing page.
Can AWS Glue handle real-time data?
Yes, AWS Glue supports streaming ETL using Apache Spark Structured Streaming. It can process data from sources like Amazon Kinesis and Apache Kafka in near real time, enabling real-time analytics and monitoring.
How does AWS Glue compare to AWS Data Pipeline?
AWS Glue is more advanced than AWS Data Pipeline. While Data Pipeline focuses on basic data movement, Glue offers full ETL automation, code generation, a metadata catalog, and support for complex transformations using Spark. Glue is the recommended service for modern data integration needs.
Amazon’s AWS Glue is a transformative tool for organizations navigating the complexities of modern data integration. From automating ETL processes to enabling real-time analytics, it offers a comprehensive suite of features that reduce manual effort and accelerate time-to-insight. Whether you’re building a data lake, migrating legacy systems, or processing streaming data, AWS Glue provides the scalability, flexibility, and ease of use needed to succeed in today’s data-driven world. By leveraging its advanced capabilities and following best practices, teams can unlock the full potential of their data assets.
Recommended for you 👇
Further Reading: