AWS Management Console: 7 Powerful Features You Must Know
Unlock the full potential of cloud computing with the AWS Management Console—a powerful, user-friendly gateway to Amazon’s vast ecosystem of services. Whether you’re a developer, sysadmin, or business owner, mastering this tool is your first step toward cloud mastery.
What Is the AWS Management Console?

The AWS Management Console is a web-based interface that allows users to interact with Amazon Web Services (AWS) in a visual, intuitive way. Instead of using command-line tools or APIs, users can manage their cloud resources—like virtual servers, storage buckets, and databases—through a graphical dashboard. It’s the go-to platform for managing AWS services without writing code.
Core Purpose and Functionality
The primary goal of the AWS Management Console is to simplify cloud management. It provides a centralized hub where users can launch instances, configure security settings, monitor performance, and manage billing—all from one place. This makes it especially valuable for teams new to AWS or those who prefer visual tools over scripting.
- Provides a graphical interface for AWS services
- Enables point-and-click configuration of cloud resources
- Supports real-time monitoring and troubleshooting
How It Compares to CLI and SDKs
While the AWS Management Console offers ease of use, it’s important to understand how it stacks up against the AWS Command Line Interface (CLI) and Software Development Kits (SDKs). The CLI and SDKs are more powerful for automation and integration into development workflows, but they require technical expertise. The console, on the other hand, lowers the barrier to entry.
“The AWS Management Console is the front door to the cloud—simple, secure, and scalable.” — AWS Official Documentation
Key Features of the AWS Management Console
The AWS Management Console isn’t just a dashboard—it’s a feature-rich environment designed to empower users at every level. From service navigation to cost tracking, its tools are built to enhance productivity and control.
Unified Service Dashboard
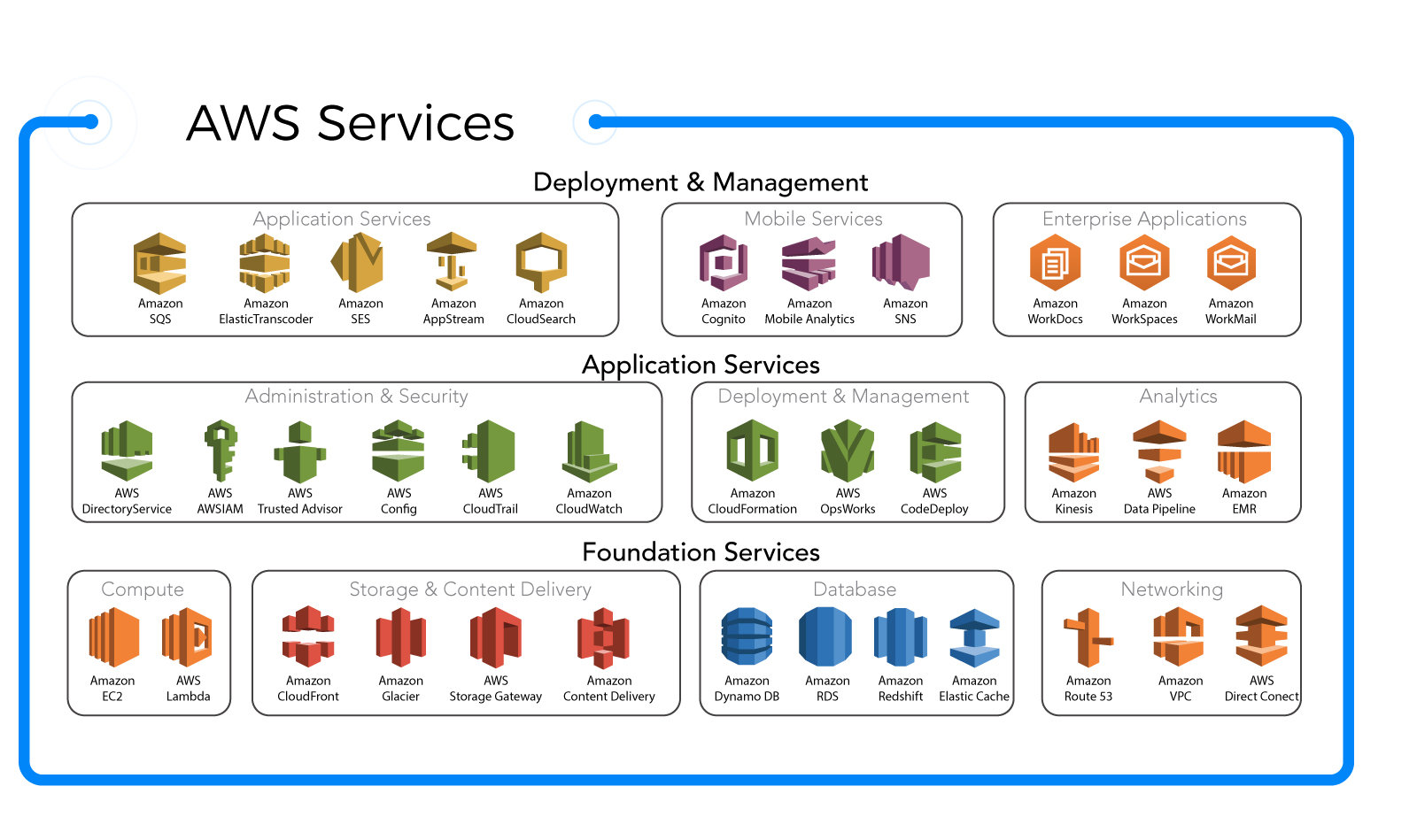
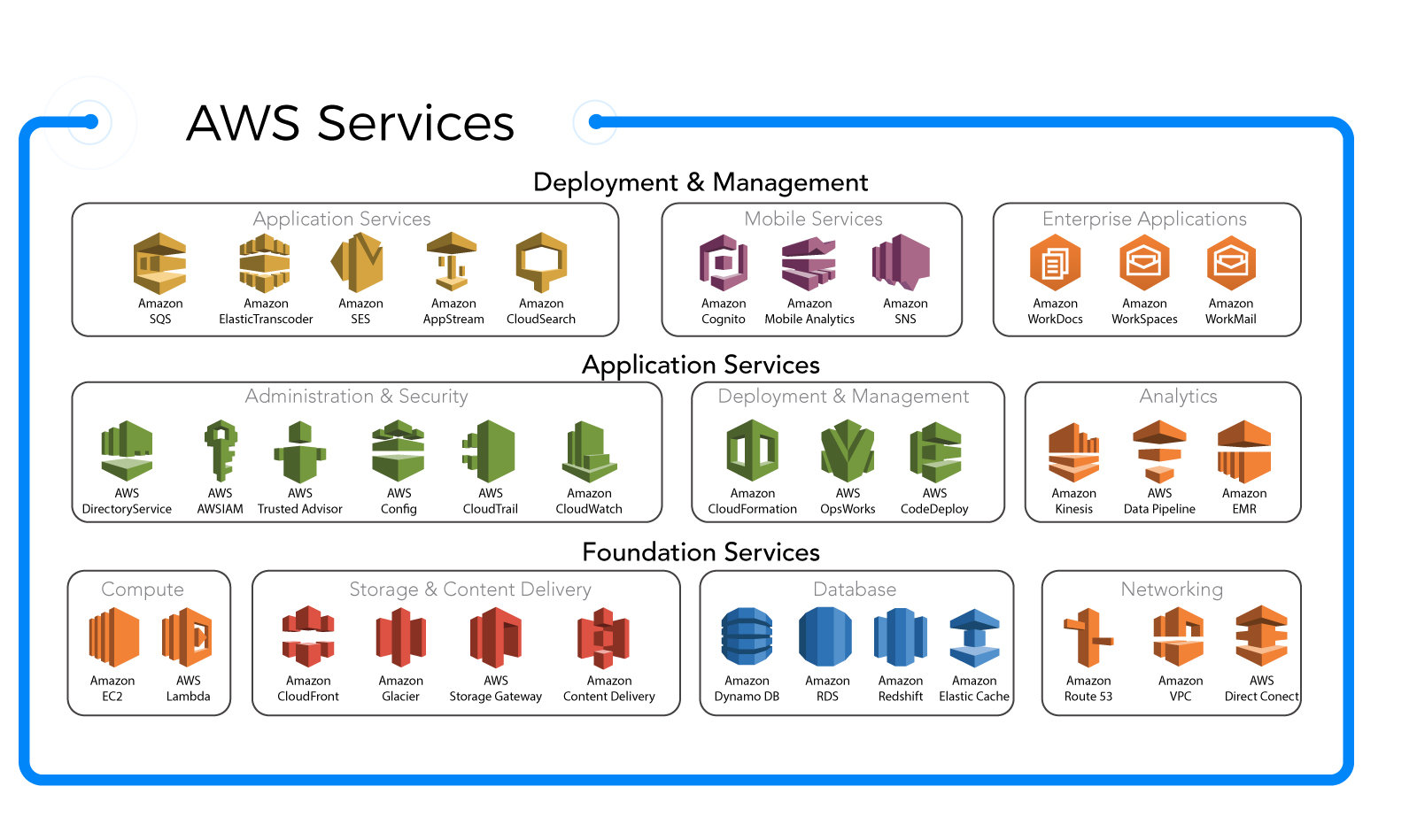
One of the most powerful aspects of the AWS Management Console is its unified dashboard. Upon logging in, users are greeted with a searchable list of all available AWS services, organized by category (e.g., Compute, Storage, Networking). This makes it easy to find and launch services like EC2, S3, or Lambda without memorizing commands.
- Search bar for quick service access
- Service categories for organized navigation
- Recent services list for faster access
Customizable Home Screen
Users can personalize their console homepage by pinning frequently used services, adding widgets, and setting up quick links. This level of customization improves workflow efficiency, especially for teams managing multiple projects.
- Add shortcuts to commonly used services
- Display cost and usage widgets
- Set default regions for faster deployment
Integrated Monitoring and Alerts
The console integrates seamlessly with Amazon CloudWatch, allowing users to monitor resource performance in real time. You can set up alarms, view logs, and receive notifications directly within the interface, reducing the need to switch between tools.
- Real-time metrics for EC2, RDS, and other services
- Visual dashboards for performance trends
- Alerts via email or SMS for critical events
Navigating the AWS Management Console Interface
Understanding the layout of the AWS Management Console is crucial for efficient cloud management. The interface is designed with usability in mind, but its depth can be overwhelming for beginners.
Main Navigation Menu
Located on the left side of the screen, the main navigation menu is your gateway to all AWS services. It’s divided into sections like Compute, Storage, Database, and Security & Identity. You can expand or collapse categories, and even search for services using the top search bar.
- Expandable service categories
- Search functionality for quick access
- Recent services for faster navigation
Region and Account Selection
In the top-right corner, users can select their AWS region and account. This is critical because resources are region-specific. Choosing the wrong region can lead to deployment errors or increased latency. The console remembers your last-used region, but it’s always wise to double-check.
- Drop-down menu for region selection
- Account switcher for multi-account setups
- Region-specific service availability alerts
User Preferences and Settings
Under the user dropdown (top-right), you can access preferences like theme (light/dark mode), console language, and notification settings. These small tweaks can significantly improve user experience, especially during long management sessions.
- Dark mode for reduced eye strain
- Language and time zone settings
- Notification preferences for billing and security
Setting Up Your First AWS Management Console Session
Getting started with the AWS Management Console is straightforward, but requires careful attention to security and access settings. This section walks you through the initial setup process.
Creating an AWS Account
To access the AWS Management Console, you first need an AWS account. Visit aws.amazon.com/console and click “Create an AWS Account.” You’ll need to provide contact information, payment details, and verify your identity via phone call or text.
- Provide valid email and phone number
- Enter credit card information for billing
- Complete identity verification
Configuring IAM Roles and Permissions
Once your account is created, the next step is setting up Identity and Access Management (IAM). IAM allows you to create users, assign roles, and define permissions. Never use the root account for daily tasks—instead, create an IAM user with administrative privileges.
- Create an IAM user with console access
- Assign the AdministratorAccess policy
- Enable multi-factor authentication (MFA)
Logging In and Navigating the Dashboard
After setting up IAM, log in using your user credentials. You’ll be directed to the AWS Management Console homepage. Take time to explore the service catalog, set your preferred region, and familiarize yourself with the layout. AWS also offers a Getting Started Guide to help new users.
- Use IAM credentials, not root account
- Select your preferred AWS region
- Explore the service catalog and search bar
Managing AWS Services Through the Console
The true power of the AWS Management Console lies in its ability to manage a wide range of cloud services. From launching virtual machines to configuring databases, the console puts control at your fingertips.
Launching and Configuring EC2 Instances
Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) is one of the most used services in AWS. Through the console, you can launch an EC2 instance in minutes. Navigate to the EC2 dashboard, click “Launch Instance,” choose an Amazon Machine Image (AMI), select instance type, configure security groups, and launch.
- Choose from Linux, Windows, or custom AMIs
- Select instance types based on CPU, memory, and cost
- Configure security groups to control inbound/outbound traffic
Creating and Managing S3 Buckets
Amazon S3 (Simple Storage Service) is used for storing and retrieving data. In the console, go to the S3 service, click “Create bucket,” name your bucket, choose a region, and set permissions. You can then upload files, set lifecycle policies, and enable versioning.
- Enable server-side encryption for security
- Set bucket policies for access control
- Use S3 Transfer Acceleration for faster uploads
Setting Up RDS Databases
Amazon RDS (Relational Database Service) simplifies database management. From the console, select RDS, click “Create database,” choose your engine (e.g., MySQL, PostgreSQL), configure instance settings, and set up backups and maintenance windows.
- Choose between single-AZ and multi-AZ deployments
- Enable automated backups and snapshots
- Monitor performance with CloudWatch integration
Security and Access Control in the AWS Management Console
Security is paramount in cloud computing. The AWS Management Console provides robust tools to manage access, enforce policies, and protect your data.
Using IAM for User and Role Management
Identity and Access Management (IAM) is the cornerstone of AWS security. Through the console, you can create users, assign roles, and define granular permissions. Best practices include using the principle of least privilege and enabling MFA.
- Create users with specific access needs
- Use IAM roles for EC2 instances and applications
- Regularly audit permissions with IAM Access Analyzer
Enabling Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
MFA adds an extra layer of security by requiring a second form of authentication. In the console, go to IAM, select your user, and enable MFA using a virtual or hardware device. This is especially critical for administrative accounts.
- Supports virtual MFA apps like Google Authenticator
- Compatible with hardware MFA devices
- Can be enforced via IAM policies
Monitoring with AWS CloudTrail and CloudWatch
AWS CloudTrail logs all API calls made in your account, including those from the console. This provides an audit trail for security investigations. CloudWatch, on the other hand, monitors resource performance and can trigger alerts based on thresholds.
- CloudTrail tracks user activity and API usage
- CloudWatch provides real-time metrics and logs
- Integrate both for comprehensive monitoring
Cost Management and Billing Insights via the Console
One of the most valuable features of the AWS Management Console is its ability to help you track and optimize costs. Cloud services can become expensive quickly if not monitored, but the console provides tools to stay in control.
Accessing the AWS Billing Dashboard
The Billing Dashboard, accessible from the console, gives you a real-time view of your AWS spending. You can see current charges, forecast future costs, and download detailed reports. It’s essential to check this regularly to avoid bill shocks.
- View current month-to-date charges
- See cost breakdown by service and region
- Download billing reports in CSV format
Setting Up Budgets and Cost Alerts
You can create custom budgets in the console to monitor spending. For example, set a monthly budget of $100 for EC2 and receive an email when you hit 80% of that limit. This proactive approach helps prevent overspending.
- Create budgets based on cost, usage, or reservations
- Set up SNS notifications for budget thresholds
- Use AWS Budgets for cost forecasting
Using Cost Explorer for Detailed Analysis
Cost Explorer is a powerful tool within the AWS Management Console that visualizes your spending trends over time. You can filter by service, region, or tag, and even project future costs based on historical data. This is invaluable for financial planning and optimization.
- Visualize 12 months of cost history
- Filter by tags for department or project tracking
- Forecast costs up to 12 months ahead
Best Practices for Using the AWS Management Console
To get the most out of the AWS Management Console, it’s important to follow industry best practices. These guidelines help improve security, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness.
Use IAM Roles Instead of Hardcoding Credentials
Never hardcode AWS access keys in applications. Instead, use IAM roles that can be attached to EC2 instances or Lambda functions. This eliminates the risk of credential leaks and simplifies permission management.
- Assign roles to EC2 instances for secure access
- Use temporary credentials via AWS STS
- Avoid storing access keys in code repositories
Enable CloudTrail for Audit Logging
Always enable AWS CloudTrail to log all actions taken in the console. This creates a detailed audit trail that can be used for compliance, troubleshooting, and security investigations. You can store logs in an S3 bucket and analyze them with Athena.
- Enable trails for all regions
- Encrypt logs with AWS KMS
- Integrate with SIEM tools for real-time monitoring
Regularly Review and Clean Up Unused Resources
Unused resources like idle EC2 instances, unattached EBS volumes, or empty S3 buckets can lead to unnecessary charges. Use the AWS Management Console to regularly audit your environment and terminate or archive unused assets.
- Identify idle resources using Cost Explorer
- Delete unattached EBS volumes and snapshots
- Archive old S3 data to Glacier for cost savings
Advanced Tips and Hidden Features
Beyond the basics, the AWS Management Console offers several advanced features that can boost productivity and streamline operations.
Using the AWS Console Mobile App
AWS offers a mobile app that mirrors many console functions. You can monitor resources, receive alerts, and even stop EC2 instances from your phone. It’s a handy tool for on-the-go management.
- Monitor CloudWatch alarms and metrics
- Start/stop EC2 instances remotely
- Receive SNS notifications on mobile
Leveraging AWS Config for Compliance
AWS Config helps you assess, audit, and evaluate the configurations of your AWS resources. Through the console, you can set up rules to check for compliance with internal policies or regulatory standards like HIPAA or GDPR.
- Track configuration changes over time
- Set up conformance packs for automated checks
- Generate compliance reports for audits
Customizing Console with Tags and Filters
Use tags to organize resources by project, environment, or owner. In the console, you can filter resources by tag, making it easier to manage large-scale deployments. For example, filter all “Production” EC2 instances to apply a security update.
- Apply tags during resource creation
- Use tag-based filtering in service dashboards
- Enforce tagging policies with AWS Config
What is the AWS Management Console?
The AWS Management Console is a web-based interface that allows users to manage Amazon Web Services through a graphical dashboard. It provides access to over 200 AWS services, enabling users to launch instances, configure security, monitor performance, and manage billing without using code.
How do I access the AWS Management Console?
You can access the AWS Management Console by visiting https://aws.amazon.com/console/ and logging in with your AWS account credentials. It’s recommended to use an IAM user account instead of the root account for security reasons.
Is the AWS Management Console free to use?
Yes, the AWS Management Console itself is free to use. You only pay for the AWS services you consume (e.g., EC2 instances, S3 storage). There is no additional charge for accessing or using the console interface.
Can I automate tasks in the AWS Management Console?
While the console is primarily designed for manual operations, you can initiate automation through integrations with AWS Lambda, CloudFormation, and Systems Manager. For full automation, it’s recommended to use the AWS CLI or SDKs in conjunction with the console.
How can I improve security in the AWS Management Console?
To enhance security, always enable multi-factor authentication (MFA), use IAM roles instead of root credentials, enable AWS CloudTrail for logging, and regularly audit permissions. Avoid sharing account credentials and enforce strong password policies.
The AWS Management Console is an indispensable tool for anyone using Amazon Web Services. From its intuitive interface to powerful management capabilities, it simplifies cloud operations while offering deep control over resources. By mastering its features—from service navigation to cost monitoring—you can optimize performance, enhance security, and reduce expenses. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced cloud engineer, leveraging the full potential of the AWS Management Console is key to success in the cloud era.
Further Reading: